
#Numpy random how to
If we know how to generate random numbers from a standard normal distribution, it is possible to generate random numbers from any normal distribution with the formula $$X = Z * \sigma + \mu$$ where Z is random numbers from a standard normal distribution, $\sigma$ the standard deviation $\mu$ the mean. Import numpy as np import matplotlib.pyplot as plt data = np.random.randn(100000) hx, hy, _ = plt.hist(data, bins=50, normed=1,color="lightblue") plt.ylim(0.0,max(hx)+0.05) plt.title('Generate random numbers \n from a standard normal distribution with python') plt.grid() plt.savefig("numpy_random_numbers_stantard_normal_distribution.png", bbox_inches='tight') plt.show() Create a matrix of random numbers from a normal distribution

All the numbers will be in the range- (0,1). Random.rand () allows us to create as many floating-point numbers we want, and that is too of any shape as per our needs. If we want a 1-d array, use just one argument, for 2-d use two parameters. How to generate random numbers from a normal (Gaussian) distribution in python ? Rand () function of numpy random Parameters It takes shape as input.

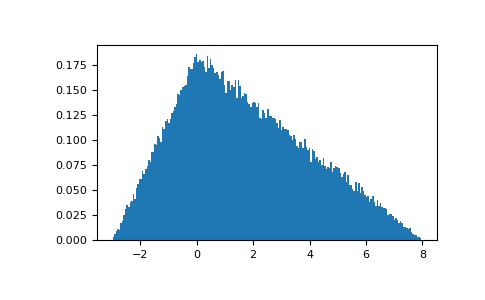
To generate a random numbers from a standard normal distribution ($\mu_0=0$, $\sigma=1$) Gives ] Create a matrix of random numbers from a standard normal distribution Note: can be also used to generate random numbers for other range, for example : data = np.random.uniform(-10,5, size=(4,3)) print(data) To create a matrix of negative and positive random floats, a solution is to use data = np.random.uniform(-1,1, size=(6,2)) print(data) Gives for example ] Create a matrix of random floats between -1 and 1 Note: to generate for example random floats between 0 and 100 just multiply the matrix by 100: data = np.random.rand(4,3) * 100.0 print(data) To create a matrix of random floats between 0 and 1, a solution is to use data = np.random.rand(4,3) print(data) Will always gives the same random numbers: Create a matrix of random floats between 0 and 1 Then data = np.random.randint(-10,10,10) print(data) To understand why go see: the "The Hitchhiker's Guide to the Galaxy (travel guide)'s book") You can choose any seed number (It is common to use 42. To do that a solution is to use : np.ed(seed=42)
#Numpy random code
The output which is generated on executing the code completely depends on the random data variables that were used by the system, and hence are input dependent. Note: to make your work reproductible it is sometimes important to generate the same random numbers. The NumPy random seed function enables the coder to optimize codes very easily wherein random numbers can be used for testing the utility and efficiency. Gives ] Create always the same random numbers To create a matrix of random integers, a solution is to use import numpy as np data = np.random.randint(-10,10,10) print(data)Īnother example with a matrix of size=(4,3) data = np.random.randint(-10,10,size=(4,3)) print(data)


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
